The pre-engineered metal building system is a building enclosure system that always includes a structural system and often includes roof and wall cladding. The structural system consists of rigid frames that are fabricated from plate steel and “cold formed” through a manufacturing process. These rigid frames consist of roof beams and columns that are field bolted together.
The pre-engineered metal building system is advantageous because it very economically allows for the creation of large column-free enclosures. The alternative structural framing choices, such as mill steel and light gauge metal, use more steel and are therefore considerably more expensive to build. The best applications for the pre-engineered metal building system include industrial applications such as complex industrial facilities, warehouses and distribution centers. The system is also used in retail stores, shopping centers, motels, auto dealerships, office complexes, airplane hangars, sports and entertainment arenas as well as schools, libraries, churches, medical facilities and government buildings.
THE COMPONENTS OF PEB SYSTEM
These PEB buildings are composed with the combination of various sections they are built up sections, hot rolled sections and the elements of cold formed sections. The basic steel frame work is provided by these elements. The PEB components may be broadly classified into following parts they are as follows:
Primary Frame – Pre-engineered steel building is portal frame construction comprises of primary and secondary framing and bracing system. A combination of these three elements and weather covering sheeting results in stable steel buildings instead of individual frame.
Secondary structural frames – Secondary framing system is mainly purlin and girt of Z or C shapes of various sizes. In Pre-engineered buildings normally cold form Z sections are used for secondary framing to achieve high strength and lower weight. Purlins/girt are members which transfers forces and moments from one frame to another frame for overall stability of the building structure and it all acts as framing system for weather covering sheeting purpose.
Roof and Wall Panels – Tin shades & Curtain Wall made of Glass & Roll-formed steel sheets usually comes in the category. From transfer of wind force and other acting loads form building frame to the foundation at certain interval. X-bracing system is used to change the direction of forces for reducing the impact of forces. Normally rod, pipes or angles are used for x-bracing purpose.
Sandwich Panels – Sandwich panel is made of three layers in which a non-Aluminium Core is inserted between two aluminium sheets.
Weather covering for roof and walls – In order to provide weather covering for roof and walls from external condition, steel structure need to be covered fully/partially as per functional requirements. For all purposes this covering provides access for all architectural and function requirements as well. Normally, metal profiled steel sheets are used for covering purpose. Now a day’s different color/color combinations are used to make building more aesthetic & elegant. There are various other elements of sheeting such as flashings, trims, ridge cover, peak panel, rack trim, drip trim etc. which is made of the same material as of sheeting and equally important for weather tight functioning of the building. In addition, proper rain water gutter for collection of rainwater and down take pipe for discharge of water from gutter to the ground is also a key element to the building for overall performance of the building. All sheetings are joined together with the help of self drilling/self tapping screw and necessary sealing material such as butyl tape, sealant, foam filler etc. are used to make buildings more efficient.
Mezzanine system – Now a day’s construction of mezzanine system is very common being used in steel building for various purposes. In most of the factory or warehouse building shop floor office, production offices, stores, maintenance office, wash rooms, canteen etc. are made above the shop floor area wherever surplus head rooms are available. This also helps in saving the floor area as well creates ease of serving being closely. This also reduces the cost of construction A typical mezzanine system is basically a joist beam construction taking support from the building columns as per availability and top of beams and joist deck slab is poured over GI decking of profiles metal sheet. A light reinforcement over decking and light concrete is used to make a permanent floor. Typical mezzanine details for various elements are shown below.
Anchoring – In order to install the steel building on RCC pedestal/foundation, it is necessary to have an anchoring system suitably designed to take up various loads and forces of the building and to transfer the same to the ground through anchor bolts arrangement. Size of anchor bolts and its quantities are designed as per reactions calculated as per building design.
Building accessories – There are various other building elements which may not be important structurally but very important functionally and it adds performance of the building. Skylight, wall light, Doors, windows, louvers, ventilators, turbo-vent, insulations, roof curb etc. are equally important to the smooth functioning of the building.
Crane system – All pre-engineered steel buildings can be designed for crane operation provision as per operational need. There is various type of crane being used in industry for various purposes- EOT overhead crane with pendant or cabin operated, Overhung/under-slung crane system, Monorail crane or hoist system, Wall mounted crane and Jib crane.
Paints and finishes – Pre-painted steel is produced on modern, high-speed coil painting lines where surface preparation prior to painting, paint application & paint curing is done on a highly automated line under optimum condition.
For the construction of these structures use of hot rolled tapered sections for primary framing and cold formed sections may be used as per the internal requirements for the stress for secondary framing, thus the control of wastage of steel and the weight of the structure and hence lighter foundations. These kinds of structures are basically rigid jointed structure frames from hot rolled or cold formed sections, the roofs and side wall cladding is supported by main and secondary frames by purlins and sheeting rails. For the selection of PEB roof slope is selected from 5 to 12 degree, because of least volume of air occupied during heating and cooling of the structure. To achieve the reduction in time of design, fabrication and installation the pre-engineered building system concentrates on the use of pre-designed connections and predetermined material stocks for structure to design and fabricate
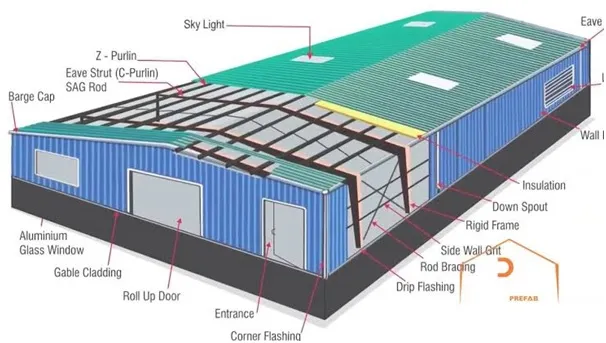
STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS OF PEB
In structural engineering, a pre-engineered building (PEB) is designed by a PEB supplier or PEB manufacturer, to be fabricated using best suited inventory of raw materials available from all sources and manufacturing methods that can efficiently satisfy a wide range of structural and aesthetic design requirements. Within some geographic industry sectors these buildings are also called pre-engineered metal buildings (PEMB) or, as is becoming increasingly common due to the reduced amount of pre-engineering involved in custom computer-aided designs, simply engineered metal buildings (EMB).
Pre-engineered buildings are factory-built buildings of steel that are shipped to site and bolted together. What distinguishes them from other buildings is that the contractor also designs the building – a practice called design & build. This style of construction is ideally suited to industrial buildings and warehouses; it is cheap, very fast to erect, and can also be dismantled and moved to another site – more on that later. These structures are sometimes called ‘metal boxes’ or ‘tin sheds’ by laymen – they are essentially rectangular boxes enclosed in a skin of corrugated metal sheeting.
Great speed is achieved because while the foundations and floor slab are being constructed, the beams and columns – the structural system – are being fabricated in the factory. Once the foundations and floor are done, the columns are shipped to the site, lifted into place by cranes, and bolted together.
The structural system of pre-engineered steel buildings give it its speed and flexibility. This system consists of factory-fabricated and factory-painted steel column and beam segments that are simply bolted together at site. The columns and beams are custom-fabricated I-section members that have an end plate with holes for bolting at both ends. These are made by cutting steel plates of the desired thickness, and welding them together to make I sections. The cutting and welding is done by industrial robots for speed and accuracy; operators will simply feed a CAD drawing of the beams into the machines, and they do the rest. This production line style of work makes for great speed and consistency in fabrication. The shape of the beams can be tailored to optimum structural efficiency: they are deeper where the forces are greater, and shallow where they are not. This is one form of construction in which the structures are designed to carry exactly the loads envisioned, and no more.
In order to accurately design a pre-engineered building, engineers consider the clear span between bearing points, bay spacing, roof slope, live loads, dead loads, collateral loads, wind uplift, deflection criteria, internal crane system and maximum practical size and weight of fabricated members. Historically, pre-engineered building manufacturers have developed pre-calculated tables for different structural elements in order to allow designers to select the most efficient I beams size for their projects. However, the table selection procedures are becoming rare with the evolution in computer-aided custom designs.
While pre-engineered buildings can be adapted to suit a wide variety of structural applications, the greatest economy will be realized when utilising standard details. An efficiently designed pre-engineered building can be lighter than the conventional steel buildings by up to 30%. Lighter weight equates to less steel and a potential price savings in structural framework.

Code for Steel structure design
The procedures and standards are adapted to analysis and design of pre-engineered buildings. The design is done by IS 800:2007, “ Code of practice for General Construction in steel Structures” as well as IS 875:1987(Part 1,2&3), “Indian Standard code of Practice for loads on Buildings and Structures”. With the various combination as specified in Indian Standard Dead load , Live load and Wind load had been considered for structure and also MBMA – 2002 (Metal Building Manufacturer Codes ) and AISC – 1989 ( American Institute of Steel Construction Manual ).
Steel Construction by Indian Standard (IS 800:2007): The Bureau of the Indian standards had adopted this Indian standard. This code had been considered by the experts in civil engineering divisional council after the methods and standards for construction are finalized by the engineers of structural department and the selection committee of structural sections. In the year 1950 Indian standard institution was initiated the programme of steel economy by establishing rational, efficient and optimum steel product standards and their use. For general construction of steel basic code is I.S 800:2007. It is the suitable document for any design in structures. The other codes governing the design of other steel structures, such as bridges, towers, silos, chimneys, etc., has influenced by this code only. In the country and abroad the developments taking place and the consideration has been given to them. Any additive and changes to the code have been included to make more useful standard.
Manual for Metal Systems of Building (2002): In this type of code practices the research is undertaken by MBMA that is metal building systems manual provides all details and design procedures for design of metal structures. The companies and other group of industries are the members of MBMA. In the load application aspects and design this provides the greater refinement and advances in loading methods. The MBMA low rise building system manual is replaced by this manual and represents the new way for criteria of design. When most of the municipalities comes to the building codes in the United States have adopted this system. In the past it won’t allow to govern the design in the building code, in the MBMA low rise buildings the pre recommended loads were often specified. There is a decrease for MBMA loads after reorganization in the system.
Conclusion
PEB can better meet the requirements of flexible separation between large openings in buildings than traditional buildings and can improve the area utilization rate by reducing the cross-sectional area of the columns and using lightweight wall panels. The effective indoor use area is improved by about 6%. The steel structure is suitable for mass production in factories, with a high degree of industrialization, and can integrate advanced products such as energy saving, waterproofing, heat insulation, doors and windows into one, complete application, integrate design, production, and construction, and improve the level of construction industry.
Image and Source – FRAMECAD, knstructuralengineers, jindal prefab, irjet, Pennar, smodiinfrasteel.in hindustanalcoxlimited


