Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a 3D model-based system that gives insight and tools to more efficiently plan, design and construct structures. The graphical simulation provided by BIM allows AEC (architecture, engineering, construction) professionals to see how their project will look in a real-life scenario. With project renders and architectural visualization, you can see the entire design even before starting the construction.
Types of Building Information Modeling [BIM] used in construction
Building Information Modeling applications allow the extraction of different views from a building model for drawing production and other uses. BIM goes beyond the planning and design phase of the project, extending throughout the building life cycle. The supporting processes of building lifecycle management include cost management, construction management, project management, facility operation Different models available are-
Geographic Building Information Modeling
GIS data is necessary for planning all operations regarding any project. BIM model integration with GIS is vital as it allows for the graphical understanding of the designing and building process of geographic conditions where a project is set to take place. BIM can also provide insight into flood-prone areas and give designers accurate information to influence a structure’s location, orientation, and even construction materials. With BIM, you may design a physical structure at an object-level through sketching. BIM data is closely tied with GIS for designing and constructing a specific object, structure, or shape. GIS services allow design and construction companies to collect accurate and valuable data that will lead to much more effective and efficient design and project management.
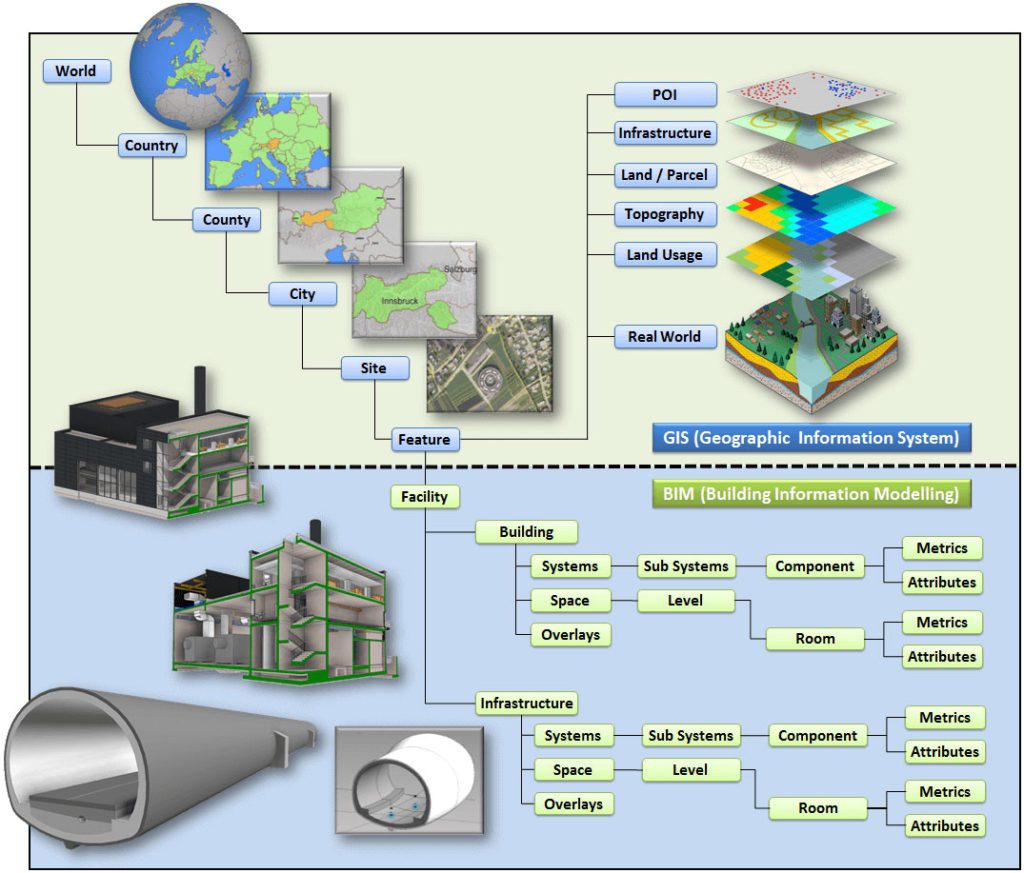
Structural Building Information Modeling
BIM is used for Structural analysis by civil engineers. It supports over 90 different steel, concrete, timber, aluminium codes. It provides various features such as Analytical Modelling, Building Planner, Autodrafter, Physical Modelling, Advanced Concrete, and Slab Design, Earthquake Mode and much more. It also comes with functions such as General arrangement drawings, Steel shop drawings, Robot Structural Analysis interoperability and many other features. Importing Options helps to take data from other applications and further maximize the work with ease. It is a nice way to design Slabs, Foundation, Beams, Columns, Walls, Ramps, etc with a variety of different shapes and types matching your needs.
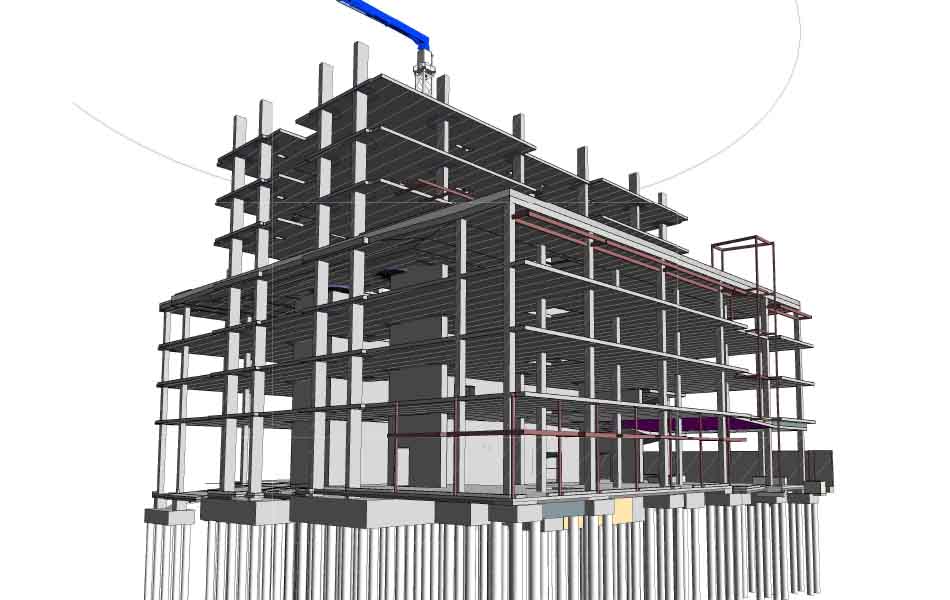

Concrete Building Information Modeling
BIM is now leveraged for accurate, detailed and constructible parametric modeling for component-oriented concrete design and plan. We can now enhance Dynamic Rebar detailing & shop drawings and create ‘intelligent’ rebar objects for incorporation. Foundation drawings are provided using assigned foundation layout, general detail and title blocks. With BIM models, quantity survey and estimation have become easy with information available such as Unit Costs, Order of Magnitude Estimates, Square Foot and Cubic Foot Estimates.
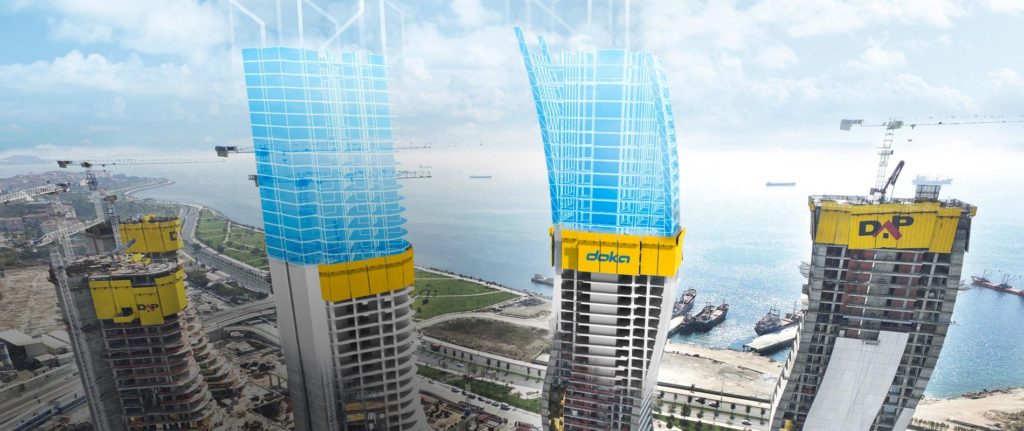

Precast Concrete Building Information Modeling
Whether it be slabs, walls or façades with BIM models helps to understand requirements in precast construction. It enables simple and rapid planning of complex precast parts with shop drawing technology. It automatically generates reports, checks for collisions and calculates numbers of parts, concrete volumes and steel weight. You can draw any conceivable geometry and any high-tech component in the highest quality, no matter how complex it is. Moreover information and planning functions available centrally for all company divisions based on 3D models which enable easy access to the data of planned projects and offer the opportunity to view their structure and status in a level of detail.

Construction Management Building Information Modeling
BIM solutions allow you to explore and evaluate a project’s constructability before it’s built. BIM can be used throughout the building life cycle, beyond the design and documentation. BIM models support construction techniques, construction planning, cost and quantity feedback, fabrication, and facilities management. Companies can now have better construction cost estimation by just analyzing the model and both parties can properly visualize the project without having it constructed. Through features such as document management, design collaboration, quality management and safety management, managing construction has become customised.

Architectural Building Information Modeling
Architects can engage with their drawings and models in the way that they always have, but the level of collaboration, input and streamlining of processes dramatically improves workflows. New options for assessment are also created, opening up new prospects for de-risking projects and delivering superior outcomes and processes. BIM can display a building’s analysis of the building’s environmental impact over time. This helps the architect find the most energy-efficient materials and most effective regenerative design features. Using BIM, one can observe the life-cycle facility management view. This display shows anticipated operational costs for the building once it’s complete. This allows architects to make wise design decisions that will lead to greater cost savings and simpler building maintenance for you in the future. Architectural BIM models for architectures come with features such as Computational design, Space planning, Energy analysis, Light and daylight analysis, Display complex spatial relationships Virtual conflict detection and resolution and Extended Reality.

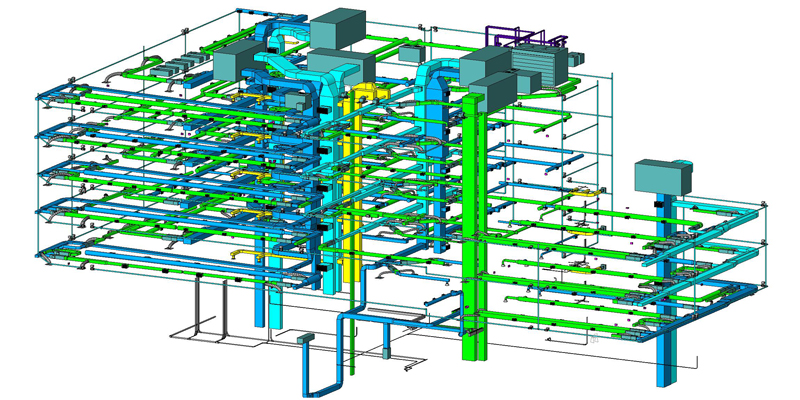
MEP Building Information Modeling
BIM allows engineers, designers and contractors in the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) fields to design building systems in their particular discipline. These solutions streamline the design, modeling, documentation, and construction of these systems and ensure they integrate seamlessly with the building it’s being placed into. With the correct software can develop data-rich MEP BIM models of the various MEP systems and carry out the coordination tasks. One can also develop data-rich MEP BIM models of the various MEP systems with 4D models.
Infrastructure Building Information Modeling
Implementing BIM on capital projects can provide benefits across planning, design, delivery, and operational areas. Access to coordinated and consistent model views by all stakeholders supports: BIM in infrastructure projects improves outcomes with its ability to investigate multiple scenarios, providing data-driven assurance that projects can be delivered on schedule and budget. Models are designed to cater to all disciplines within the civil engineering industry including Road, Rail, Drainage, Utilities etc. The information used in this initial stage of planning evolves in various steps. In the design part, you will obtain virtual models that are constructible, and then these models will serve as the prospective database to carry out the maintenance of the asset in a more efficient way. Implementing BIM on capital projects can provide benefits across planning, design, delivery, and operational areas. Connecting diverse and distributed teams to the project requires data continuity: consistently accurate data that is accessible at any time, by anyone, working anywhere. Using BIM, the information inherent in the model provides the foundation for today’s web-based and mobile collaboration tools, with a model-centric approach to better coordinate large, diverse, and distributed team workflows.

Conclusion
BIM system provides a project from the outset, a-greater control and precision to project members. They can-manage-more efficiently some variables like cost, quality and time. There are threefold advantages for engineers, contractors and owners.
Benefits to Engineers – Engineers use BIM to determine structural loads or the requirements for the design. Features of BIM-like automated assembly and digital production are used by engineers to process manufacturing information and coordinate the sequence of different systems with fabricators and subcontractors.
Benefits to Contractors – Contractors also use BIM for calculating quantity take-offs and estimating costs for bidding purposes, and planning out project schedules as well as for field management. BIM also improves planning and scheduling of subcontractors.
Benefits to Owners – Implementing BIM provides a competitive advantage to companies by enabling them to offer new services to owners and guaranteeing owners maximum return on their investment.
Image Source: largoconcrete.com, doka.com, aga-cad.com, bimservicesindia.com, autodesk.net, autodesk.com, mdx.ac.uk

